Can You Get Braces Again After Oral Surgery
With your teeth, you tin can cut, crush, and grind nutrient to set up it for swallowing and digestion. Also, your teeth play an important role in talk and make y'all await good. There are two sets of teeth. The start ready is known as babe, milk, primary, or deciduous teeth. The main teeth start to erupt at about half dozen months of age. These teeth are later replaced past the permanent teeth (the second prepare). As well, there are four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Each type has a specific part. Usually, teeth can withstand high chewing force. Nonetheless, bacterial acids can damage the teeth, causing dental caries and abscess. To understand how caries and other dental problems occur, you should know the tooth anatomy. In this article we will discuss:
- What are the types of teeth and their functions?
- Molar anatomy: the construction of a tooth and surrounding tissues.
- When the primary and permanent teeth erupt?
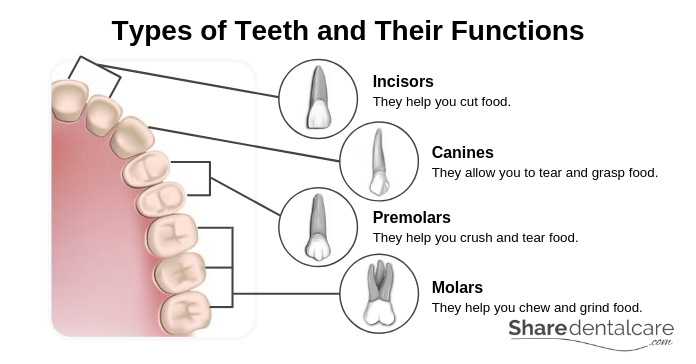
Types of Teeth and Their Functions
The main task of teeth is to cut, crush, and grind food, making swallowing and digestion easier. Also, they help the states grin and talk. Every molar in the oral cavity has a specific function:
- Incisors: they are in the front area of the upper and lower jaw (4 in each arch). Incisors are abrupt and allow food biting and cutting.
- Canines: they are located direct after the incisors. Canines are conical-shaped. They hold nutrient during biting to facilitate the cutting of food.
- Premolars and molars: they are located backside canines. They accept a broad and flat surface (occlusal surface) with several cusps. They crush nutrient betwixt the occlusal surfaces of upper and lower premolars and molars to brand food swallowing and digestion easier.
Tooth Anatomy
The teeth are different in shape. Nevertheless, they have the same tooth anatomy.
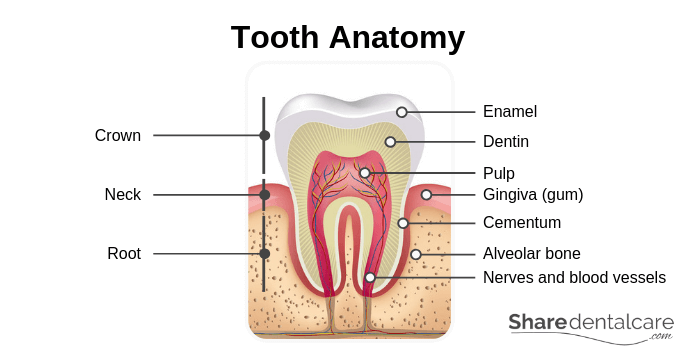
Tooth Anatomy: Parts of a Tooth
Each molar consists of 3 anatomical parts: the crown, cervix, and root.
- The crown: it is the visible portion of the tooth that protrudes from the gum. The crown is covered past enamel, the hardest substance in the human body.
- The cervix: it is the expanse where the crown joins the root. The neck is surrounded past gingiva (glue).
- The root: it is the lower 2-thirds of the tooth. It is surrounded by the jaw os. Incisors and canines have ane root. Molars are multi-rooted (2-3 roots). The number of roots is different from a person to some other.
Tooth Beefcake: Molar Layers
The tooth is made of several layers of varying density and hardness: the enamel, dentin, cementum, and lurid.
The Enamel
The enamel is the outer layer of teeth that covers the crown. As well, information technology protects the tooth confronting external dissentious forces. Tooth enamel is the almost resistant and hardest tissue in the homo body. It consists of 95% inorganic substance (mainly calcium and phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite), i% organic substance, and four% h2o. The fluoride increases the hardness of tooth enamel past converting the hydroxyapatite crystals to fluorapatite. So, fluoride toothpaste tin increase the strength of enamel. In contrast, acid can harm the enamel past detaching calcium and phosphate, causing dental caries. The tooth enamel is exposed to 2 processes:
- Demineralization: when oral bacteria decompose carbohydrates in food debris and produce acid, the oral pH drops below five.v. The bacterial acid dissolves the enamel surface, which leads to the loss of calcium and phosphate ions, causing early phase of dental caries. This is known as "demineralization". (pH is a measure of the acidic or bones graphic symbol of an aqueous solution. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic).
- Remineralization: when the oral pH rises, the enamel restores minerals (calcium and phosphate) from saliva, reversing the early stage of dental caries.
Dentin
The dentin is the 2d layer of the tooth, after the enamel. Information technology is the largest part of molar construction, surrounding the pulp. It contains fine tubes chosen "dentinal tubules" which contain nerve tissues. The nerve tissues provide stimuli to the pulp. The dentin is sensitive to heat, cold, and touch, which appears equally pain sensation. The dentin is softer and more susceptible to dental caries than the enamel. This is due to the slightly different composition of dentin.
Cementum
The cementum is a calcified substance that covers the root. Information technology attaches the tooth to the alveolar os. Cementum is softer than the dentin and enamel.
Dental Pulp
Within the tooth, there is a sleeping accommodation known equally the pulp chamber. It contains nervus tissues and blood vessels that nourish the tooth. These nerve tissues and blood vessels are extending from the jaw bone to the pulp through a minor hole at the root tip.
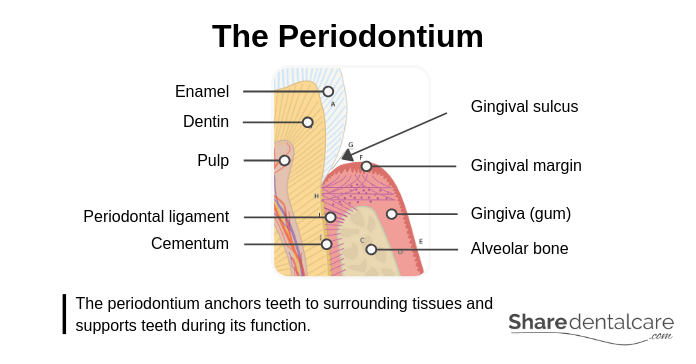
The Periodontium: Tissues that Environment and Support Teeth
The periodontium anchors teeth to surrounding tissues and supports teeth during its function. The periodontium consists of:
- Gingiva: it is a part of the oral mucosa that surrounds teeth and covers the maxilla and mandible. The beautiful smile comes from a harmonious coexistence of teeth and gingiva. Healthy strong gingiva is pink in color, has a harmonious moving ridge profile, and doesn't bleed. Inflamed gingiva is ruby, soft, and bleeding frequently during tooth brushing.
- Cementum: information technology is a thin layer that covers the roots of the tooth. Likewise, information technology attaches the molar to the bone.
- Periodontal ligament (PDL): information technology is also known as periodontal fibers. Information technology is connective tissue fibers in the minor gap between the cementum and the jaw bone. The periodontal ligament provides an attachment of the tooth to the jaw bone. Too, it has a supporting, nutritive, sensory, and remodeling function.
- Alveolar Bone: the alveolar os supports teeth and is covered by the gingiva. Information technology's well supported with blood and subjected to continuous modification. The pressure during mastication is transmitted to the os and stimulates its modification which makes the bone stronger. When there is no pressure level on the bone because of tooth loss, the bone recedes. Os loss may make it difficult to anchor a dental implant or hold a denture.
Molar Eruption
The kid has 20 chief teeth. In each jaw, at that place are four incisors, 2 canines, and 4 molars. These teeth are gradually replaced past permanent teeth betwixt the ages of half dozen and 12 years former (mixed dentition). Normally, the adult has 32 permanent teeth. In each jaw, there are iv incisors, 2 canines, 4 premolars, and 4 molars.
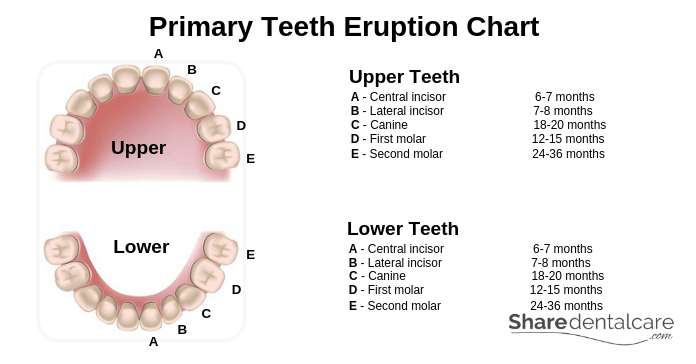
The Eruption of Primary Teeth
Upper Primary Teeth
- Central incisor: vi-seven months
- Lateral incisor: 7-eight months
- Canine: eighteen-20 months
- Beginning Molar:12-15 months
- Second Molar: 24-36 months
Lower Primary Teeth
- Central incisor: 6-7 months
- Lateral incisor: 7-eight months
- Canine:18-xx months
- Get-go Molar: 12-15 months
- 2nd Molar: 24-36 months
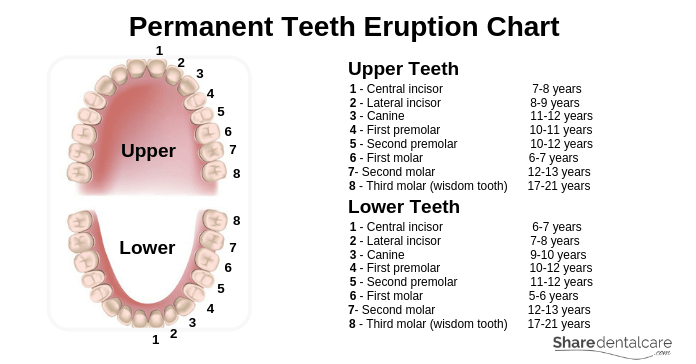
The Eruption of Permanent Teeth
Upper Permanent Teeth
- Primal incisor: 7-8 years
- Lateral incisor: viii-9 years
- Canine: 11-12 years
- First premolar:10-11 years
- Second premolar: 10-12 years
- Showtime molar: 6-vii years
- Second tooth: 12-13 years
- 3rd molar (wisdom molar): 17-21 years
Lower Permanent Teeth
- Central incisor: half-dozen-vii years
- Lateral incisor: 7-8 years
- Canine: nine-10 years
- First premolar: ten-12 years
- Second premolar: 11-12 years
- First molar: 5-vi years
- Second molar: 12-13 years
- Third molar (wisdom molar): 17-21 years
Conditions
To understand how dental problems occur, yous should know the tooth anatomy. Common dental weather condition include:
- Dental caries: leaner in the oral cavity decompose nutrient debris and produce acids. These acids dissolve the enamel, causing the formation of dental caries. Untreated caries may extend to the dentin and pulp, causing hurting and sensitivity to hot and cold. The handling of caries includes the removal of dental caries and placement of a tooth filling to restore the shape and function.
- Tooth abscess: when bacteria enter the lurid, it may lead to the germination of molar abscess at the root tip. Your dentist may perform a root canal treatment to eliminate the infection or extract the tooth if it is severely damaged. A molar abscess may as well occur every bit a outcome of gum disease.
- Gum illness: it is an inflammation of the gums caused by leaner in the dental plaque. Symptoms of mucilage disease include bleeding gums, glue recession, and bad breath. If mucilage affliction is left untreated, information technology may lead to the destruction of the periodontal ligament, alveolar bone loss, and eventually molar loss. The treatment of gum disease includes scaling and root planing.
- Teeth grinding: information technology involves grinding or clenching your teeth. Over fourth dimension, teeth grinding can wear down the enamel, leading to toothache, tooth sensitivity, and molar loss.
Conclusion
Teeth play an important part in digestion. Incisors help you cut the food. Canines allow you to grasp and tear food. Premolars and molars grind food to make swallowing and digestion easier. Also, our teeth help us talk and brand us await good. Teeth are different in shape. All the same, they have the same tooth anatomy. Every tooth consists of three parts: the crown, neck, and root. Also, every tooth made of several layers: the enamel, dentin, cementum, and pulp. Knowing the tooth anatomy will help you empathize how dental issues occur and how the handling is performed.
Source: https://sharedentalcare.com/tooth-anatomy/
0 Response to "Can You Get Braces Again After Oral Surgery"
Post a Comment